Solid Liquid Gas

The states of matter are a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry, and are typically classified into three main categories: solid, liquid, and gas. Each state of matter has distinct properties and characteristics that set it apart from the others. In this article, we will explore the properties and behaviors of solids, liquids, and gases, and discuss the transitions that occur between these states.
Properties of Solids
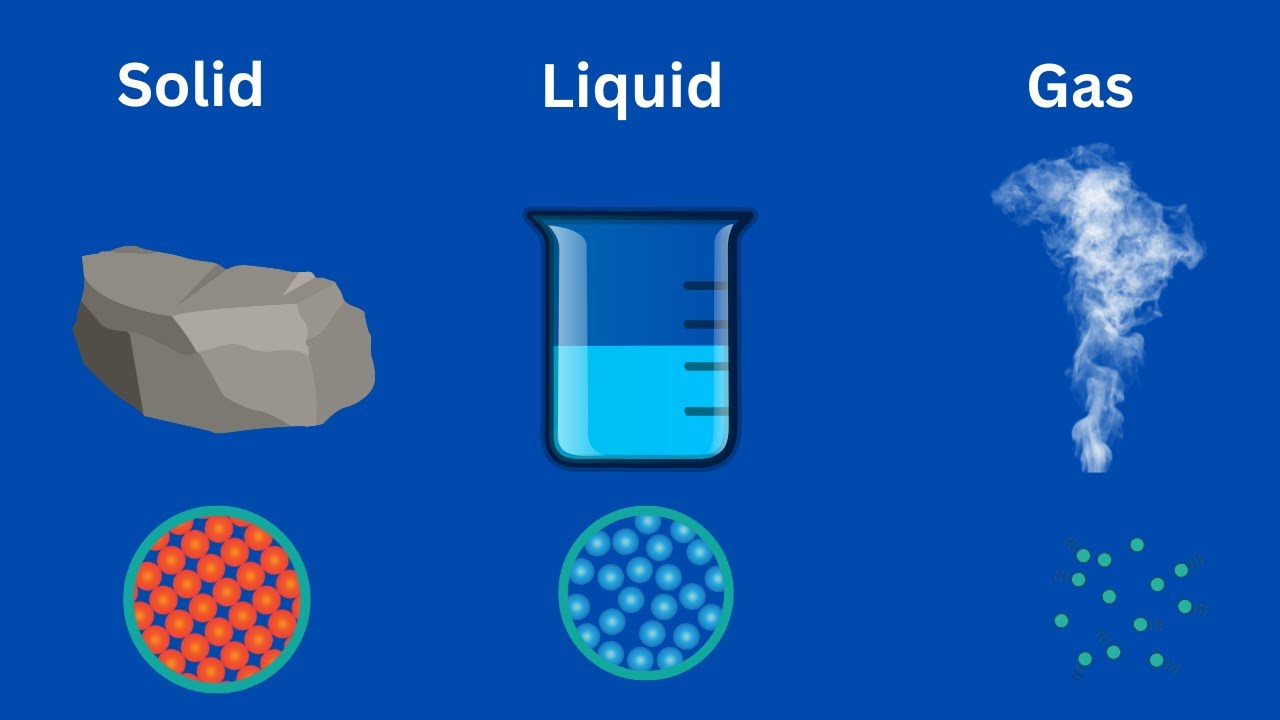
Solids are characterized by their rigidity and resistance to changes in shape and volume. The particles that make up a solid are closely packed and have a fixed position in space, with a strong attraction between them. This attraction gives solids their shape and structure, and allows them to maintain their form even when external forces are applied. Examples of solids include rocks, metals, and ice.
One of the key properties of solids is their density, which is defined as the mass per unit volume of the substance. Solids tend to have high densities due to the close packing of their particles. Another important property of solids is their melting point, which is the temperature at which the solid changes state to become a liquid.
Types of Solids
There are several types of solids, including crystalline solids, which have a regular and repeating arrangement of particles, and amorphous solids, which lack a regular structure. Crystalline solids tend to have a more ordered and symmetrical arrangement of particles, while amorphous solids have a more random and disordered arrangement.
Some examples of crystalline solids include diamonds and quartz, while examples of amorphous solids include glass and rubber. The properties and behaviors of these different types of solids can vary significantly, and are influenced by the arrangement and interactions of their particles.
| Property | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | High | Lower than solid | Low |
| Shape | Fixed | Takes shape of container | No definite shape |
| Volume | Fixed | Fixed | Variable |

Properties of Liquids

Liquids are characterized by their ability to flow and take the shape of their container. The particles that make up a liquid are close together but are free to move past one another, allowing the liquid to flow and change shape. Examples of liquids include water, oil, and juice.
One of the key properties of liquids is their viscosity, which is a measure of their resistance to flow. Liquids with high viscosities tend to flow more slowly and have a more resistance to changes in shape, while liquids with low viscosities flow more easily and have less resistance to changes in shape.
Types of Liquids
There are several types of liquids, including polar liquids, which have a separation of charge between their particles, and nonpolar liquids, which lack a separation of charge. Polar liquids tend to have a higher viscosity and surface tension than nonpolar liquids, due to the stronger attractions between their particles.
Some examples of polar liquids include water and ammonia, while examples of nonpolar liquids include oil and gasoline. The properties and behaviors of these different types of liquids can vary significantly, and are influenced by the arrangement and interactions of their particles.
Properties of Gases
Gases are characterized by their ability to expand and fill their container. The particles that make up a gas are widely spaced and are free to move in any direction, allowing the gas to expand and contract. Examples of gases include air, helium, and oxygen.
One of the key properties of gases is their pressure, which is a measure of the force exerted by the gas on its container. Gases with high pressures tend to have a greater force exerted on their container, while gases with low pressures have a lesser force exerted on their container.
Types of Gases
There are several types of gases, including ideal gases, which behave according to the ideal gas law, and real gases, which deviate from ideal behavior. Ideal gases tend to have a simpler and more predictable behavior than real gases, due to the assumptions and simplifications made in the ideal gas law.
Some examples of ideal gases include helium and neon, while examples of real gases include air and carbon dioxide. The properties and behaviors of these different types of gases can vary significantly, and are influenced by the arrangement and interactions of their particles.
What is the main difference between a solid and a liquid?
+
The main difference between a solid and a liquid is the arrangement and movement of their particles. Solids have particles that are closely packed and have a fixed position in space, while liquids have particles that are close together but are free to move past one another.
What is the definition of viscosity?
+
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. It is defined as the ratio of the shear stress to the shear rate, and is typically measured in units of poise or pascal-seconds.
What is the ideal gas law?
+
The ideal gas law is a mathematical equation that describes the behavior of ideal gases. It is given by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature.


