Pauli Exclusion Principle
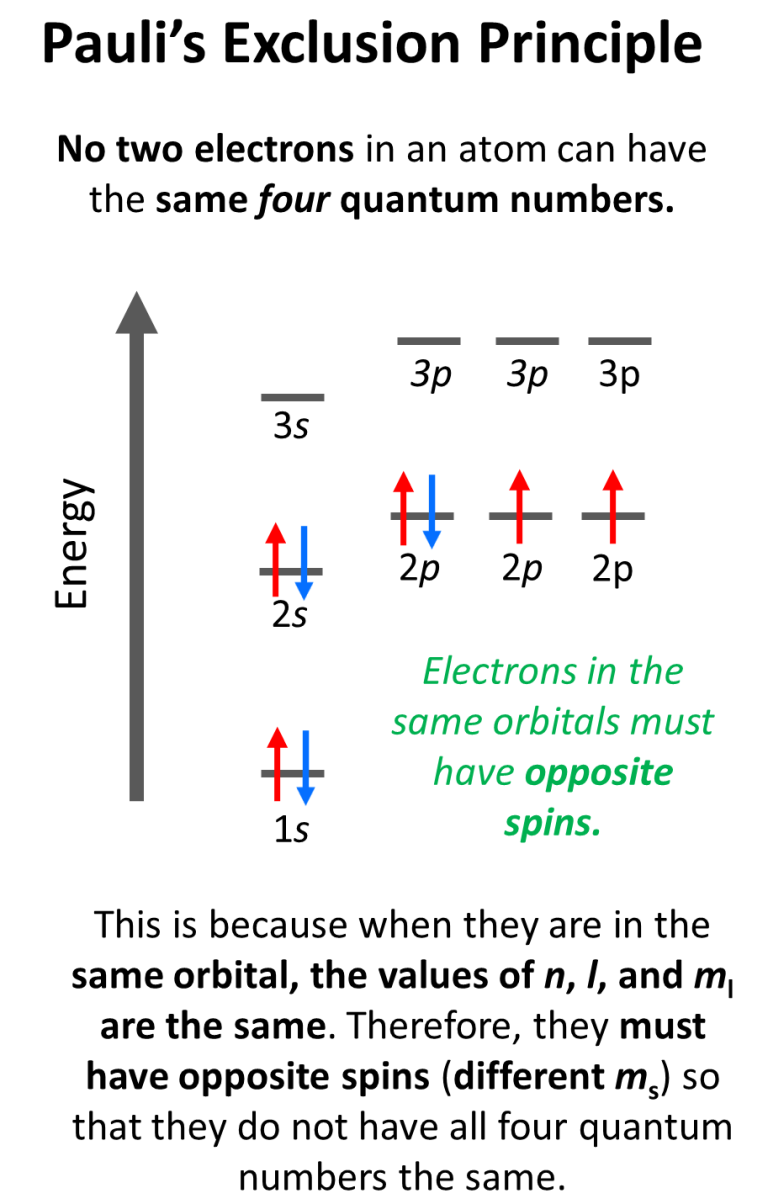
The Pauli Exclusion Principle is a fundamental concept in physics, specifically in the realm of quantum mechanics. It states that no two fermions, which are particles with half-integer spin, can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. This principle was first proposed by Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli in 1925 and has since become a cornerstone of modern physics.
Introduction to the Pauli Exclusion Principle

The Pauli Exclusion Principle is a result of the spin-statistics theorem, which relates the spin of a particle to its statistical behavior. According to this theorem, particles with half-integer spin, such as electrons, protons, and neutrons, are subject to Fermi-Dirac statistics, which dictates that no two particles can occupy the same quantum state. This is in contrast to particles with integer spin, such as photons, which are subject to Bose-Einstein statistics and can occupy the same quantum state.
Implications of the Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Pauli Exclusion Principle has far-reaching implications in various fields of physics, including atomic physics, solid-state physics, and particle physics. In atomic physics, the principle explains the structure of atoms, where electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells. The principle also explains the periodic table of elements, where elements with similar chemical properties have similar electron configurations.
In solid-state physics, the Pauli Exclusion Principle is responsible for the behavior of electrons in metals, where it explains the formation of energy bands and the concept of Fermi energy. The principle also plays a crucial role in the understanding of superconductivity, where electrons form Cooper pairs, which are subject to Bose-Einstein statistics.
| Particle Type | Spin | Statistics |
|---|---|---|
| Electron | 1/2 | Fermi-Dirac |
| Proton | 1/2 | Fermi-Dirac |
| Neutron | 1/2 | Fermi-Dirac |
| Photon | 1 | Bose-Einstein |

Applications of the Pauli Exclusion Principle

The Pauli Exclusion Principle has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, chemistry, and materials science. In physics, the principle is used to explain the behavior of particles in high-energy collisions, such as those found in particle accelerators. It is also used to understand the properties of exotic matter, such as neutron stars and white dwarfs.
In chemistry, the Pauli Exclusion Principle is used to explain the behavior of electrons in molecules, which is essential for understanding chemical bonding and reactivity. It is also used to understand the properties of materials, such as conductivity and magnetism.
Experimental Evidence for the Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Pauli Exclusion Principle has been experimentally verified numerous times, and it is now widely accepted as a fundamental principle of physics. One of the earliest experiments to verify the principle was the Stern-Gerlach experiment, which demonstrated the spin of particles and the resulting behavior of fermions.
Other experiments, such as the Lamb shift experiment and the Zeeman effect experiment, have also verified the principle. These experiments have shown that the principle is a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics and is essential for understanding the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic level.
- Stern-Gerlach experiment
- Lamb shift experiment
- Zeeman effect experiment
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
+The Pauli Exclusion Principle is a fundamental concept in physics that states that no two fermions can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously.
What are the implications of the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
+The Pauli Exclusion Principle has far-reaching implications in various fields of physics, including atomic physics, solid-state physics, and particle physics. It explains the structure of atoms, the periodic table of elements, and the behavior of electrons in metals.
What are some applications of the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
+The Pauli Exclusion Principle has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, chemistry, and materials science. It is used to explain the behavior of particles in high-energy collisions, the properties of exotic matter, and the behavior of electrons in molecules.

