Hydrogen Bonds: Unlock Molecular Secrets

Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of molecules. These bonds are responsible for the unique properties of water, the stability of DNA and proteins, and the recognition of molecules by cells. In this article, we will delve into the world of hydrogen bonds, exploring their definition, types, and importance in various biological and chemical processes.
Introduction to Hydrogen Bonds
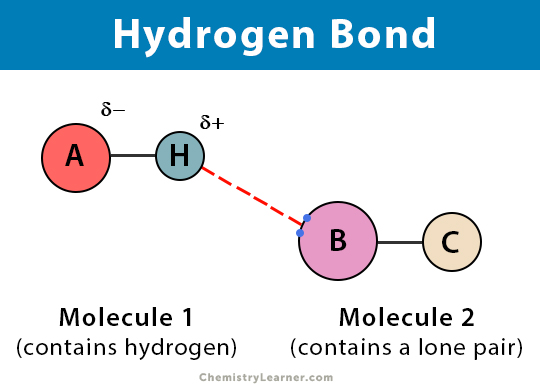
Hydrogen bonds are a type of non-covalent interaction between molecules, characterized by a weak electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and another electronegative atom. This attraction is typically between 1-5 kilocalories per mole, which is much weaker than covalent bonds. Despite their weakness, hydrogen bonds are essential for the stability and function of many biological molecules.
Types of Hydrogen Bonds
There are several types of hydrogen bonds, including:
- Intramolecular hydrogen bonds: These occur within a single molecule, where a hydrogen atom is attracted to an electronegative atom within the same molecule.
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonds: These occur between two or more molecules, where a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to an electronegative atom in another molecule.
- Hydrogen bonding networks: These are complex networks of hydrogen bonds that form between multiple molecules, often in biological systems.
Hydrogen bonds can also be classified based on their strength, with strong hydrogen bonds typically forming between highly electronegative atoms and weak hydrogen bonds forming between less electronegative atoms.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Biology

Hydrogen bonds play a vital role in many biological processes, including:
- Protein structure and function: Hydrogen bonds help stabilize the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of proteins, enabling them to perform their biological functions.
- DNA structure and replication: Hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases (adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine) hold the two strands of DNA together, allowing for the replication and transmission of genetic information.
- Cell signaling and recognition: Hydrogen bonds facilitate the recognition of molecules by cells, enabling cell signaling and communication.
| Molecule | Hydrogen Bonding Role |
|---|---|
| Water | Hydrogen bonds between water molecules give water its unique properties, such as high surface tension and boiling point. |
| DNA | Hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases stabilize the double helix structure of DNA. |
| Proteins | Hydrogen bonds help stabilize protein structure and facilitate protein-ligand interactions. |
Hydrogen Bonds in Chemical Processes
Hydrogen bonds also play a crucial role in various chemical processes, including:
- Catalysis: Hydrogen bonds can facilitate the formation of transition states, enabling chemical reactions to occur more efficiently.
- Supramolecular chemistry: Hydrogen bonds are used to assemble complex molecular structures, such as supramolecular polymers and nanoparticles.
- Separation and purification: Hydrogen bonds can be exploited to separate and purify molecules, such as in chromatography and crystallization.
In conclusion, hydrogen bonds are a vital component of molecular interactions, playing a crucial role in the structure and function of biological molecules and facilitating various chemical processes. Understanding the principles of hydrogen bonding is essential for appreciating the complex interactions that underlie many biological and chemical phenomena.
What is the strength of a hydrogen bond?
+The strength of a hydrogen bond is typically between 1-5 kilocalories per mole, which is much weaker than covalent bonds.
What types of molecules can form hydrogen bonds?
+Molecules with highly electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and fluorine, can form hydrogen bonds with hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to other electronegative atoms.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure?
+Hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases (adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine) hold the two strands of DNA together, allowing for the replication and transmission of genetic information.
